dd5950d661b777d51d9e43677425d36a122dcdea
Stepcraft GRBLizer
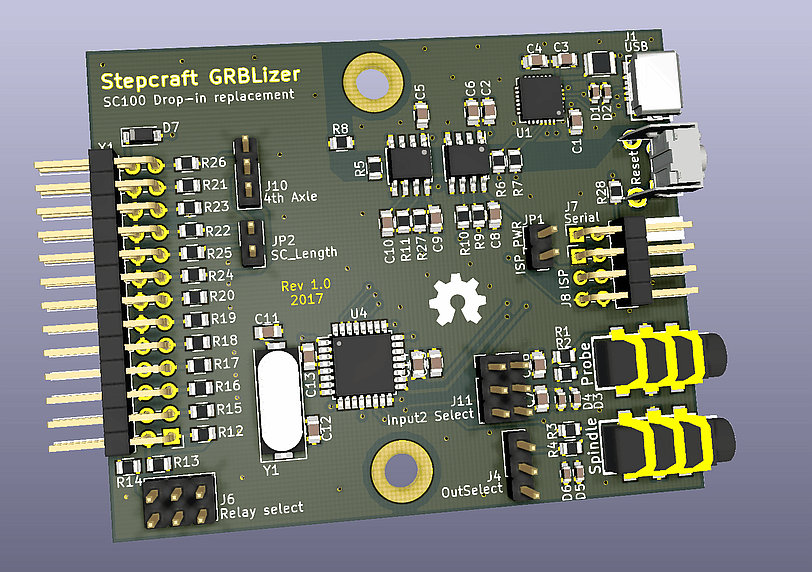
A GRBL compatible controller for use as a drop-in replacement for the SC100 USB standard controller deliverd with Stepcraft CNC machines. This Arduino Uno compatible controller is wired conforming the GRL v0.9+ standard. The controller can be used with the GRBL firmware and with EstlCAM.
Features
- The PC is fully electrically isolated from the CNC machine (optional).
- All inputs protected with clamping diodes and resistors.
- Probe inputs have a 100 Ohm / 100nF low pass filter to suppress spurious triggering. (Filter values may be experimented with.)
- 3.5mm Jack for spindle / laser / hot-end control
- 3.5mm Jack input for 2 probes.
- Serial interface fed out the back (TTL, not protected). For people in a hurry: CP2102 and isolator ICs can be left unpopulated.
- Standard 6 pin ISP programming connector fed out the back (not protected).
- Some juper block for IO-config
Stepcraft 420 CNC settings with GRBLizer
Notes kindly provided by Albin Stigö on getting GRBL v1.1 working with the GRBLizer board.
Tested on Stepcraft 420, but probably works with most other Stepcraft types.
Setup
- Stepcraft 420 CNC
- Stepcraft drivers with GRBLizer board
- GRBL v1.1
- Universal-G-Code-Sender
Install GRBL in the usual way. However you need to make some changes in config.h and cpu_map.h.
/* cpu_map.h */
// The Stepcraft has all limits on one pin.
#define X_LIMIT_BIT 1 // Uno Digital Pin 9
#define Y_LIMIT_BIT 1 // Uno Digital Pin 9
#define Z_LIMIT_BIT 1 // Uno Digital Pin 9
/* config.h */
// Since all limit switches end up being shared on one pin,
// we can only home one direction at a time.
#define HOMING_CYCLE_0 (1<<Z_AXIS) // REQUIRED: First move Z to clear workspace.
#define HOMING_CYCLE_1 (1<<Y_AXIS) // OPTIONAL: Then move X,Y at the same time.
#define HOMING_CYCLE_2 (1<<X_AXIS) // OPTIONAL: Uncomment and add axes mask to enable
// The stop output of the Stepcraft board is inverted to what GRBL expects.
// However you simply can't swap the switch because the driver board will also
// disable the motors so nothing will move.
#define INVERT_CONTROL_PIN_MASK (1<<CONTROL_RESET_BIT) // Default disabled.
GRBL settings
I haven't done a lot of fine tuning but these seems to work well enough.
$0 = 50 (Step pulse time, microseconds)
$1 = 100 (Step idle delay, milliseconds)
$2 = 0 (Step pulse invert, mask)
$3 = 0 (Step direction invert, mask)
$4 = 1 (Invert step enable pin, boolean)
$5 = 1 (Invert limit pins, boolean)
$6 = 0 (Invert probe pin, boolean)
$10 = 1 (Status report options, mask)
$11 = 0.010 (Junction deviation, millimeters)
$12 = 0.002 (Arc tolerance, millimeters)
$13 = 0 (Report in inches, boolean)
$20 = 0 (Soft limits enable, boolean)
$21 = 0 (Hard limits enable, boolean)
$22 = 1 (Homing cycle enable, boolean)
$23 = 1 (Homing direction invert, mask)
$24 = 120.000 (Homing locate feed rate, mm/min)
$25 = 900.000 (Homing search seek rate, mm/min)
$26 = 250 (Homing switch debounce delay, milliseconds)
$27 = 1.000 (Homing switch pull-off distance, millimeters)
$30 = 1000 (Maximum spindle speed, RPM)
$31 = 0 (Minimum spindle speed, RPM)
$32 = 0 (Laser-mode enable, boolean)
$100 = 133.333 (X-axis travel resolution, step/mm)
$101 = 133.333 (Y-axis travel resolution, step/mm)
$102 = 133.333 (Z-axis travel resolution, step/mm)
$110 = 800.000 (X-axis maximum rate, mm/min)
$111 = 800.000 (Y-axis maximum rate, mm/min)
$112 = 800.000 (Z-axis maximum rate, mm/min)
$120 = 10.000 (X-axis acceleration, mm/sec^2)
$121 = 10.000 (Y-axis acceleration, mm/sec^2)
$122 = 10.000 (Z-axis acceleration, mm/sec^2)
$130 = 300.000 (X-axis maximum travel, millimeters)
$131 = 420.000 (Y-axis maximum travel, millimeters)
$132 = 140.000 (Z-axis maximum travel, millimeters)
Description
Replacement ('Arduino') controller that fits inside a Stepcraft CNC machine. Comptatible with GRBL and EstlCAM
Languages
KiCad Layout
100%